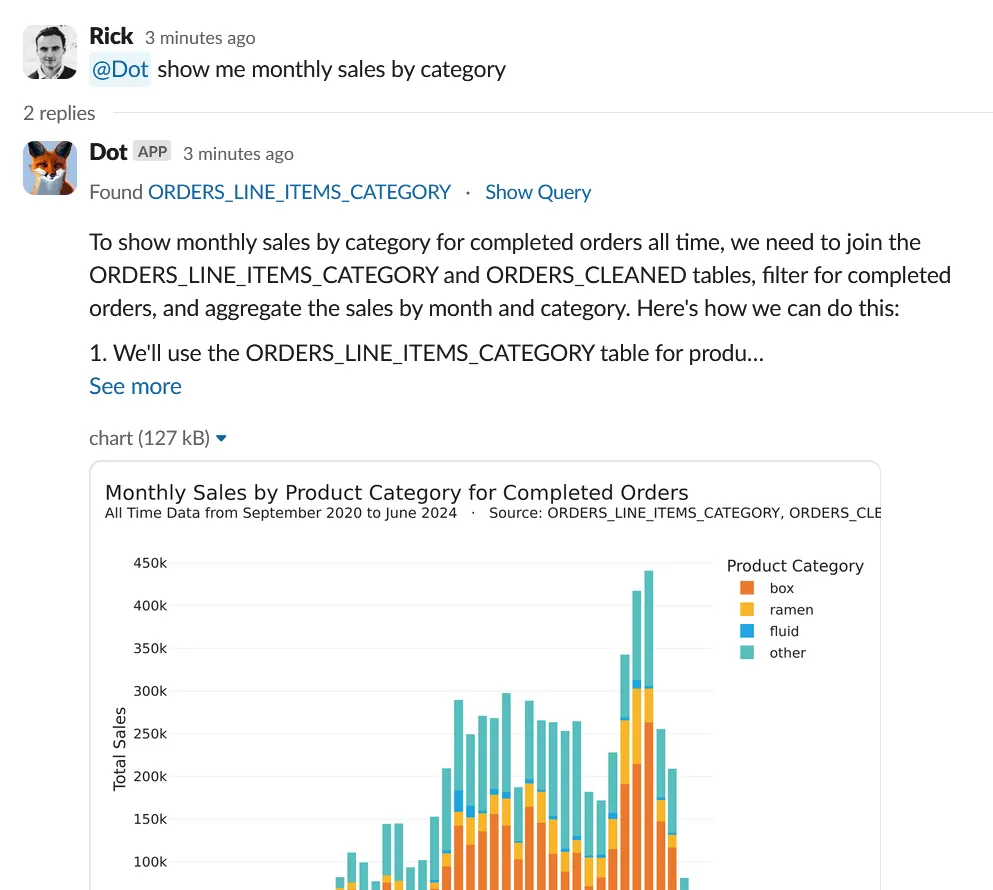
Conversational Analytics with LLMs in 2025: From Data-Chat to Decision Acceleration
What is Conversational Analytics? Two things:
- Chatting with AI data analytics agents
- Analyzing conversations (voice or text)
Now both are possible because of recent advances in AI. The need for 2 is partially a result of the explosion of new chat applications.
Why it matters
With chat-first user interfaces becoming the front door to data and customer interactions, leaders are racing to turn unstructured dialogues into structured signals that drive revenue, retention, and speed. The past 18 months have moved conversational analytics from niche add-on to board-level priority, powered by LLMs.
1. LLM-powered self-service BI goes mainstream
“Chat with your data”, “Talk to your data”, “AI analytics agents”, “Conversational Analytics”, “Text 2 SQL” all seem to head in a similar direction of allowing anybody to ask questions about the companies data sources, ideally a data warehouse or semantic layer
Zooming in there are multiple approaches:
SQL-based agents. In its simplest form this agent gets the DDL of a database, generates a query (also called text-to-sql), runs it and shows the results. That’s the approach we started with at Dot and we have refined it for the last 2.5 years to reduce hallucinations, proactively deal with data quality issues, disambiguate complexities, correct runtime errors and in general make the agent more reliable and powerful.
A really important detail is also the user interface of these agents, here you can find the following flavors:
- API: submit a natural language question and get back a SQL statement
- Web UI: ChatGPT-like web applications or copilot side panels
- Slack/Microsoft Teams: the agent is a bot that users can directly chat with, like a co-worker
- E-Mail: similar to Slack and Microsoft Teams, you write an email with the request and get back an insight
- Scheduled/Triggered: users don’t even ask a question, and just get a custom PDF report delivered with data visualizations and tables
Semantic-layer agents. Because most data models are ambiguous and LLMs can hallucinate, industry leaders have pondered the idea that a semantic layer is the critical ingredient to ensure trust in the answer of the agentic systems.
The most prominent semantic layer is Google’s Looker Semantic Layer. It’s used by 1000s of organization in production. However, it should not be confused with the similarly named product Looker Studio that focuses more on easy drag and drop visualizations and less on data modelling.
The new Gemini in Looker preview reportedly lets any employee “chat with your business data”, automatically generating “governed SQL and visualizations on top of LookML metrics”.
From our own experience with enabling Dot in production today’s semantic layers (including the dbt semantic layer and cube’s semantic layer) can be part of the solution of aligning on a source of truth, but are far from sufficient on solving the trust problem.
Clearly defined metrics are a great stepping stone, but today’s technical implementations are a bit rigid and can both limit the things that can be analyzed and still leave room for interpretation by the LLM. What’s more important is a good data model with clear business definitions.
2. Conversation insights shift from sampling to 100 % coverage
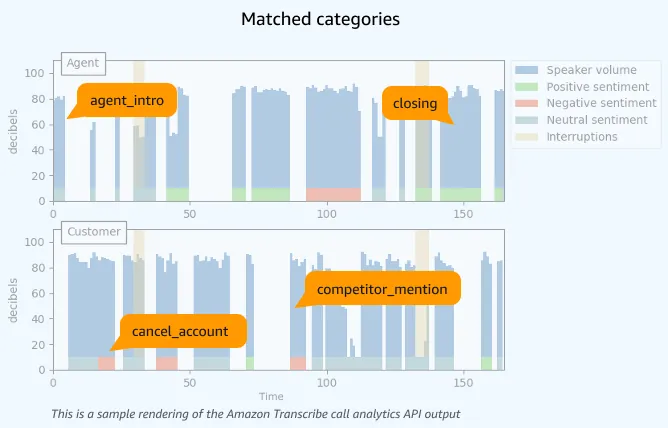
In the past, when we captured calls or chat conversations, we had rather limited options to make sense of those. With today’s LLMs and Speech-to-Text models like Whisper we can go much deeper.
Generative conversational analytics is a quality-management accelerator for call centers and sales optimizations: auto-transcribing every call, scoring sentiment/compliance and surfacing real-time coaching cues. Enterprises now treat “listen to everything, coach in the moment” as table stakes rather than an aspirational goal.
At the same time, we have more chat bots and ever making sense of these rich user interactions requires more than counting bag of words.
Outlook
Related reading:
Conversational analytics is moving from reactive reporting to proactive decision acceleration. Platforms that marry governed data semantics, real-time LLM reasoning, and embedded action channels will define the next competitive edge. Organisations that start small but design for explainability and scale will own the conversational advantage by 2026.
Rick Radewagen
Rick is a co-founder of Dot, on a mission to make data accessible to everyone. When he's not building AI-powered analytics, you'll find him obsessing over well-arranged pixels and surprising himself by learning new languages.
